FRM-Option
Properties of options
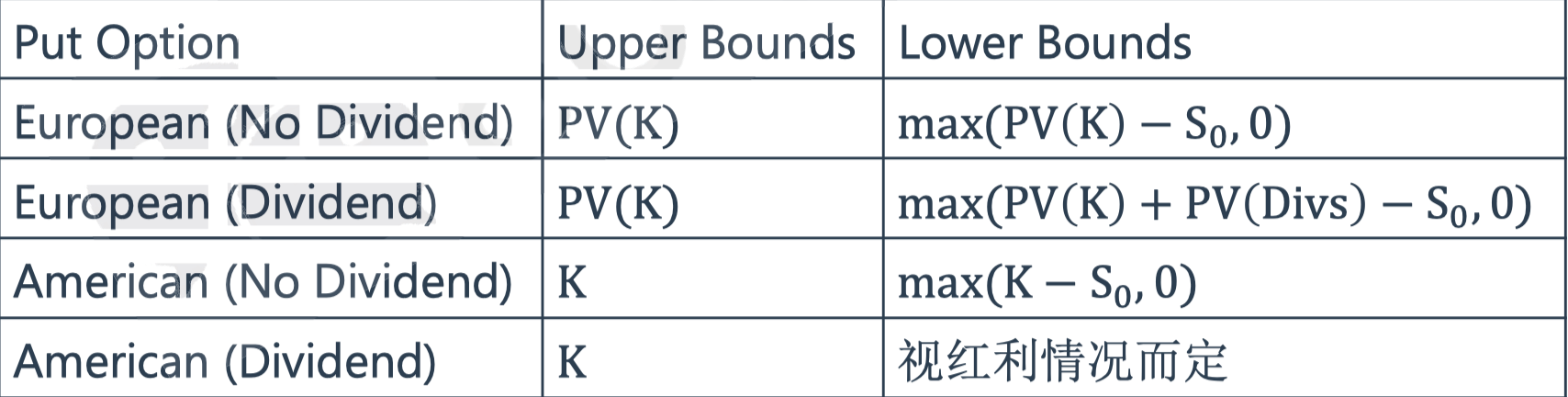
Call options
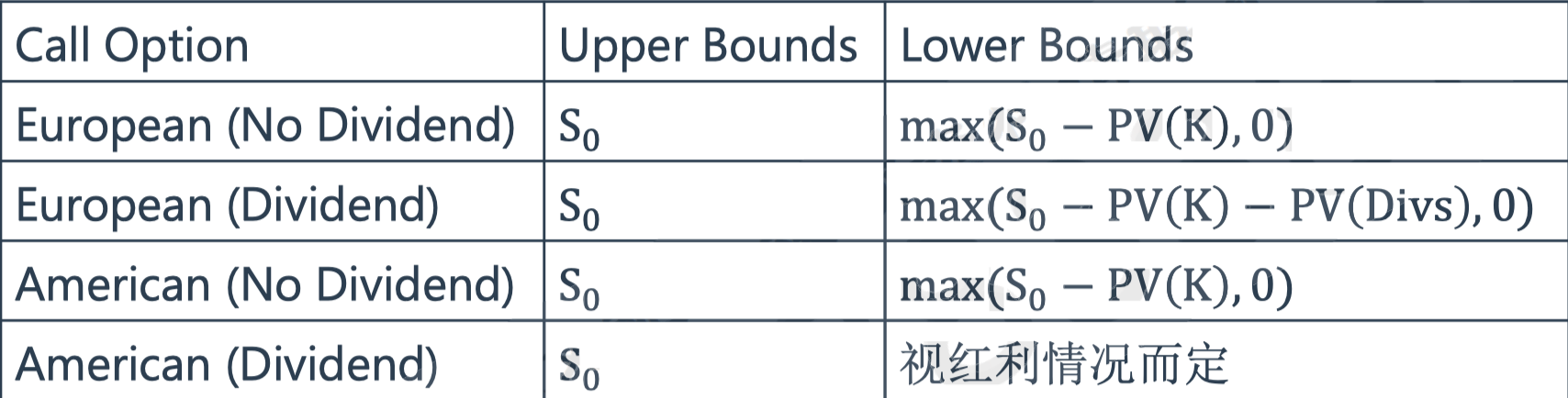
Put options
Put-call Parity
\[ P+S=C+PV(K) \]
European option -- same underlying, strike, maturity
Div adjustment
- discrete: \(P+S-D=C+Ke^{-rt}\)
- discrete rate q: \(P+Se^{-qt}=C+Ke^{-rt}\)
annual compound: \(P+S=C+\frac{K}{(1+R_f)^t}\)
American option: no exact relationship
Portfolio construction
\[ P+S=C+Ke^{-rt} \\ P=C+Ke^{-rt}-S \]
long put = long call, long zero-compound bond, short stock
Arbitrary
\[ P+S (buy)<C+Ke^{-rt}(sell) \]
###Pricing

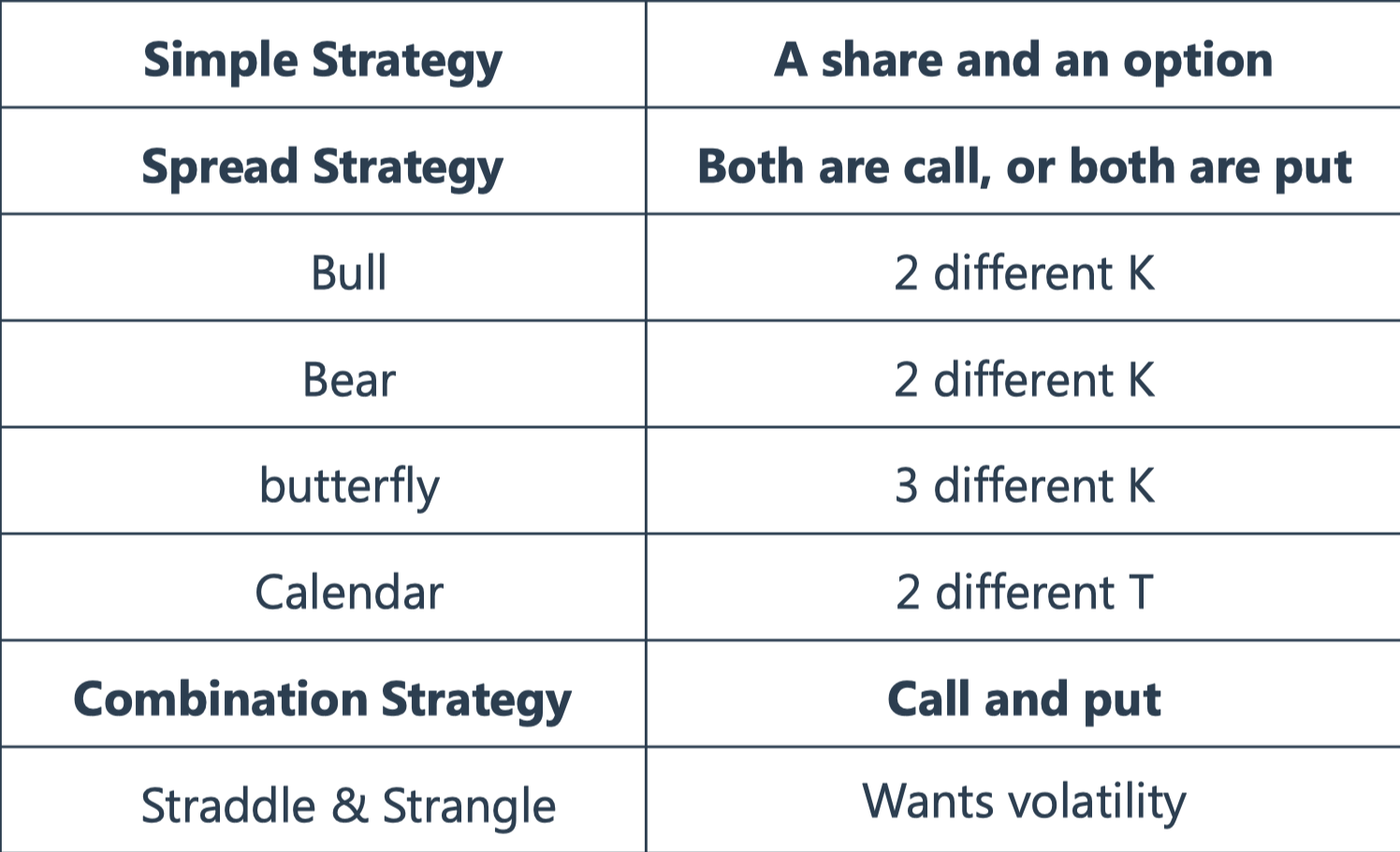
Simple Strategies
option + underlying
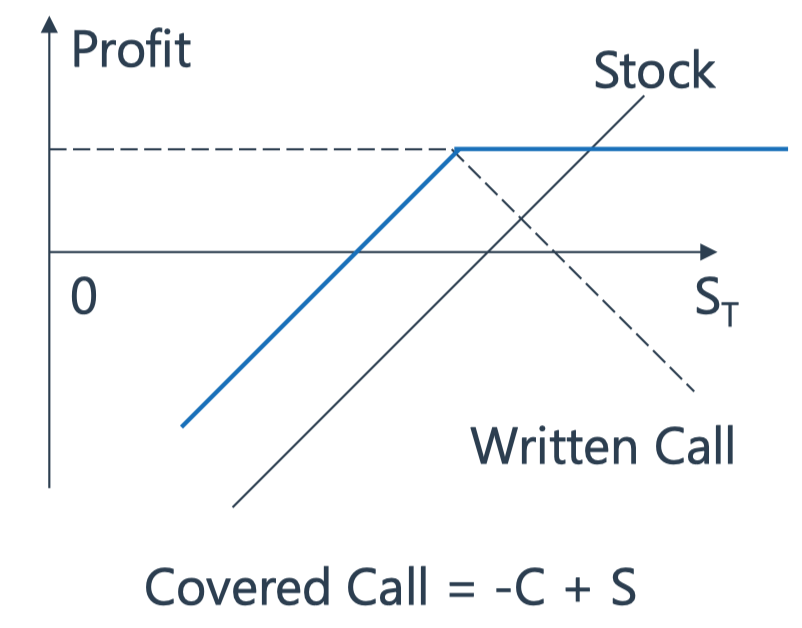
Covered Call
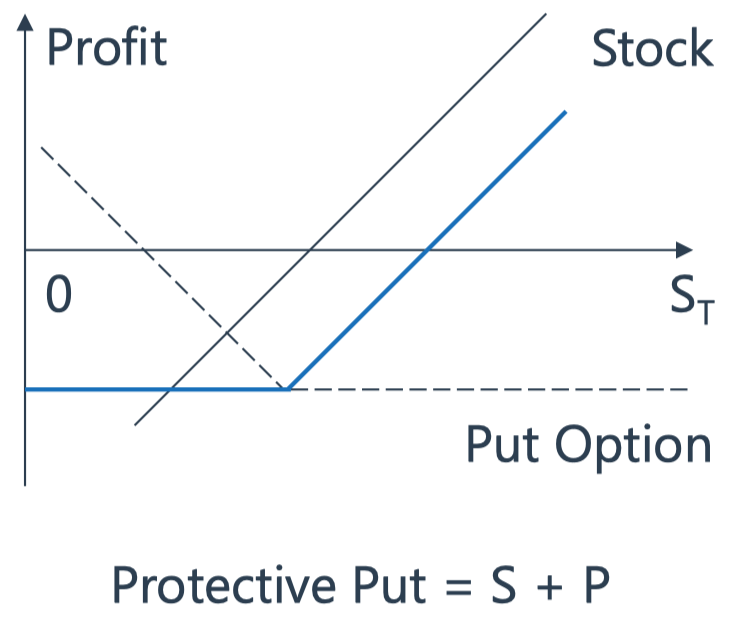
Protective Put
Principal Protected Notes(PPN)
- A PPN is structured as a zero-coupon bond and an option with a payoff that is linked to an underlying asset, index, or benchmark.
- It guarantees a minimum return equal to the investor's initial investment (the principal amount), regardless of the performance of the underlying assets.
Spread Strategies
Bull spread
outlook is bullish, buy low sell high ~ 低买高卖,行权价格
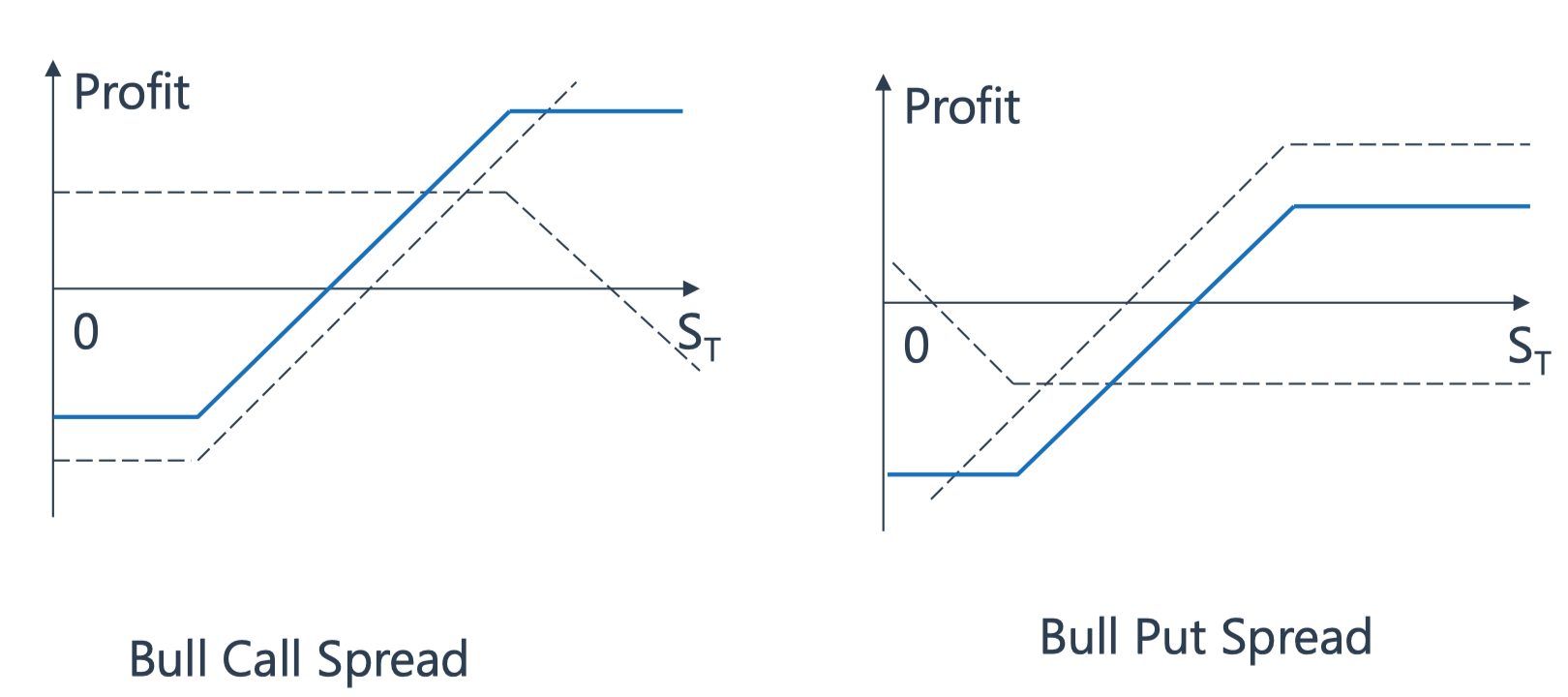
Bear Spread
outlook is bearish, buy high, sell low
Box spread
- A box spread is a combination of a bull call spread with strike prices \(K_1\) and \(K_2\) and a bear put spread with the same two strike prices.
- The payoff from a box spread is always \(K_2 – K_1\) .
- Box spread = Bull spread + Bear spread
Butterfly Spread
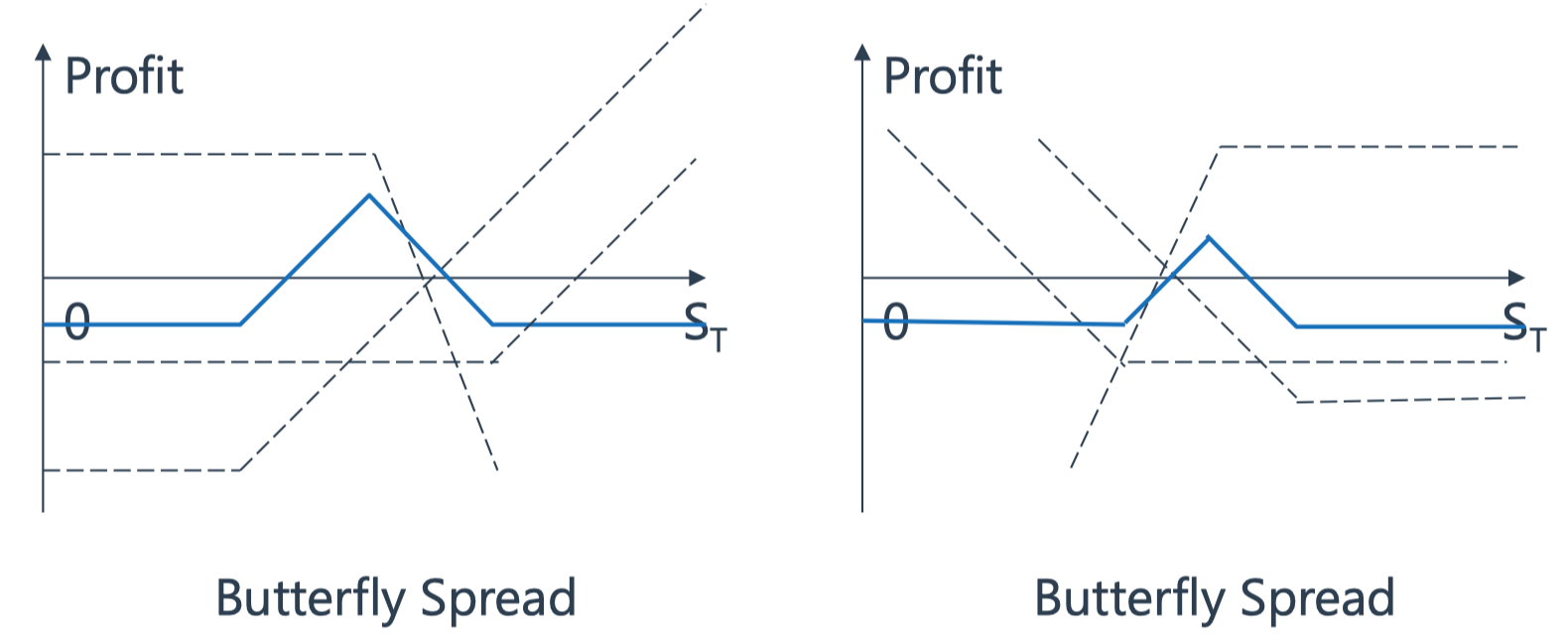
long option \(k_1\), long option \(k_3\), short option \(k_2\), \(k_2=\frac{k_1+K_3}{2}\)
Expects low volatility
Capped risk
Calender Spread
long long-term, short short-term
Combination Spread
Call+Put
Straddle and Strangle
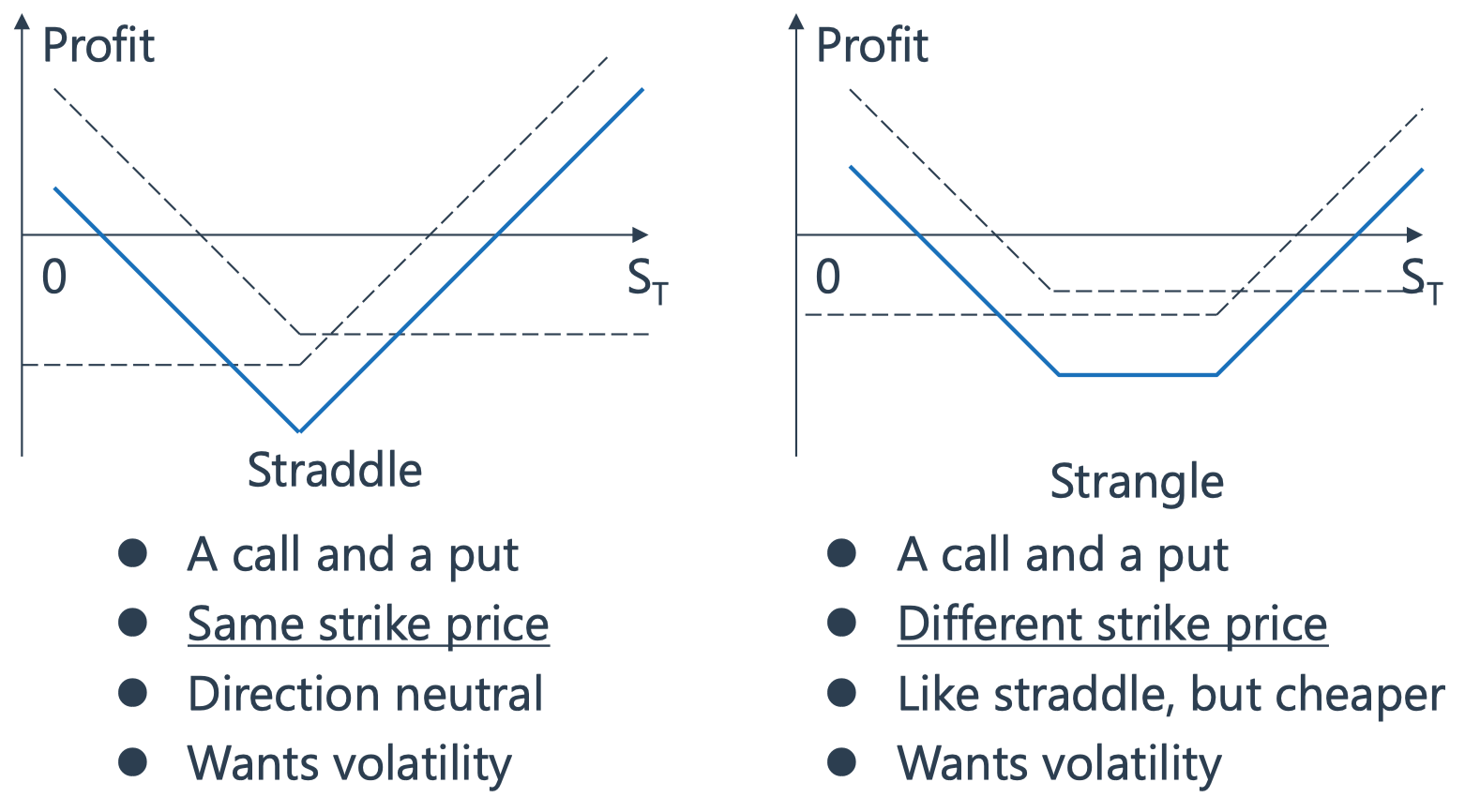
Strangle is cheaper than straddle——购买高行权价格的看涨期权,购买低行权价格的看跌期权,期权费更加便宜。
Exotic Option
Gap Option
- Call gap option
- \(S_T>K_2\), \(Payoff=S_T-K_1\)
- Put option
- \(S_T<K_2\), \(Payoff=K_1-S_T\)
Forward Start option
A forward start option is an advance purchase of a put or call option that will become active at some specified future time. It is essentially a forward on an option
Compound option
Options on options
A call on a call, a put on a call, a call on a put, and a put on a put
If both options are exercised, the total premium will be more than the premium on a single option
Chooser option
After a specified period of time, the holder can choose whether the option is a call or a put.
Barrier Option
Payoffs and existence depend on whether the underlying’s asset price reaches a certain barrier level over the life of the option.
A knock-out option ceases to exist when the underlying asset price reaches a certain barrier while a knock-in option comes into existence only when the underlying asset price reaches a barrier.
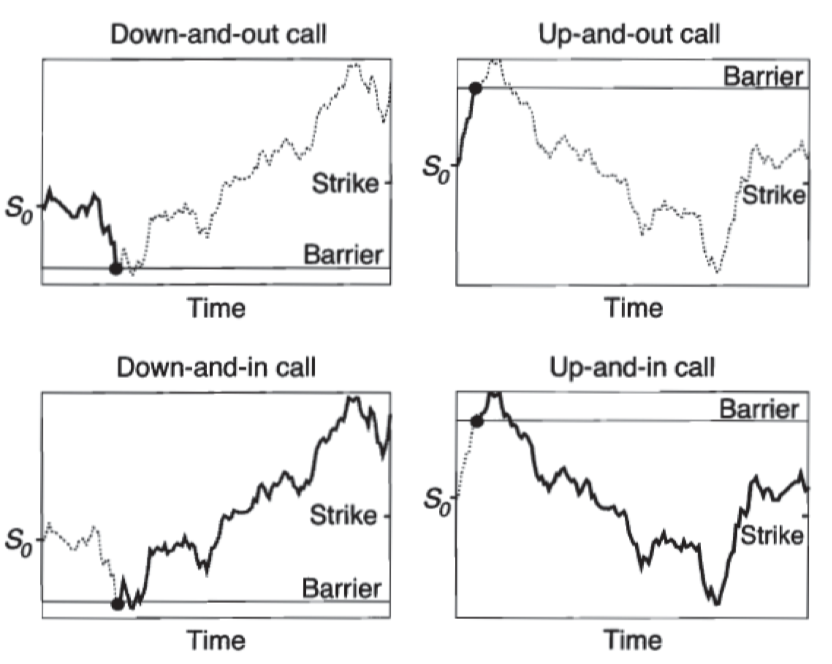
==In-out parity==
down-and-out call + doan-and-in call = call option
Binary options
- ==Cash-or-Nothing== : Pays some fixed amount of cash if the option expires in-the-money.
- ==Asset-or-Nothing== : Pays the value of the underlying security.
- A regular European call option is equivalent to a long position in an asset-or-nothing call and a short position in a cash-or-nothing call.
- A regular European put option is equivalent to a long position in a cash-or-nothing put and a short position in an asset-or-nothing put.
Call option = long asset or nothing call + short cash or nothing call
Put option = long cash or nothing put + short asset or nothing put
Lookback options
- Payoffs depend on maximum or minimum price of the underlying asset
- With floating strike and with fixed strike
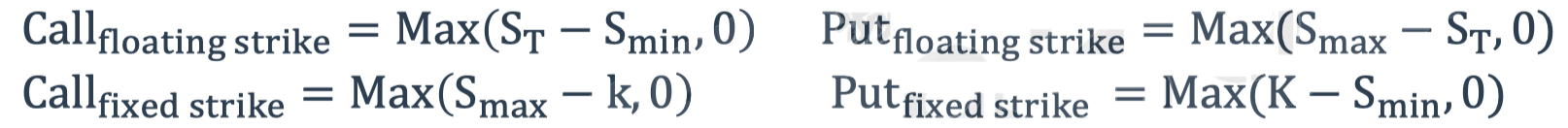
Asian options
- Payoff dependon arithmetic average of the underlying asset price
- Average price option and average strike option.
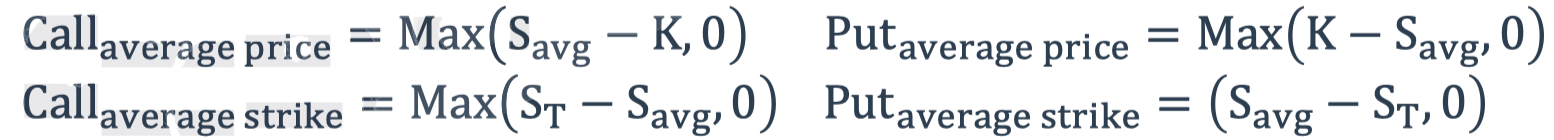
==Path-dependence==
Volatility and Variance Swap
Volatility Swap
Exchanging of volatility based on a national principal
Payments base on pre-specified volatility and realized volatility.
Variance Swap
- Exchanging pre-specified fixed variance rate for realized variance rate
Static options Replication
This technique involves searching for a portfolio of actively traded options (regular options) that approximately replicates the exotic option. Shorting this position provides the hedge.

